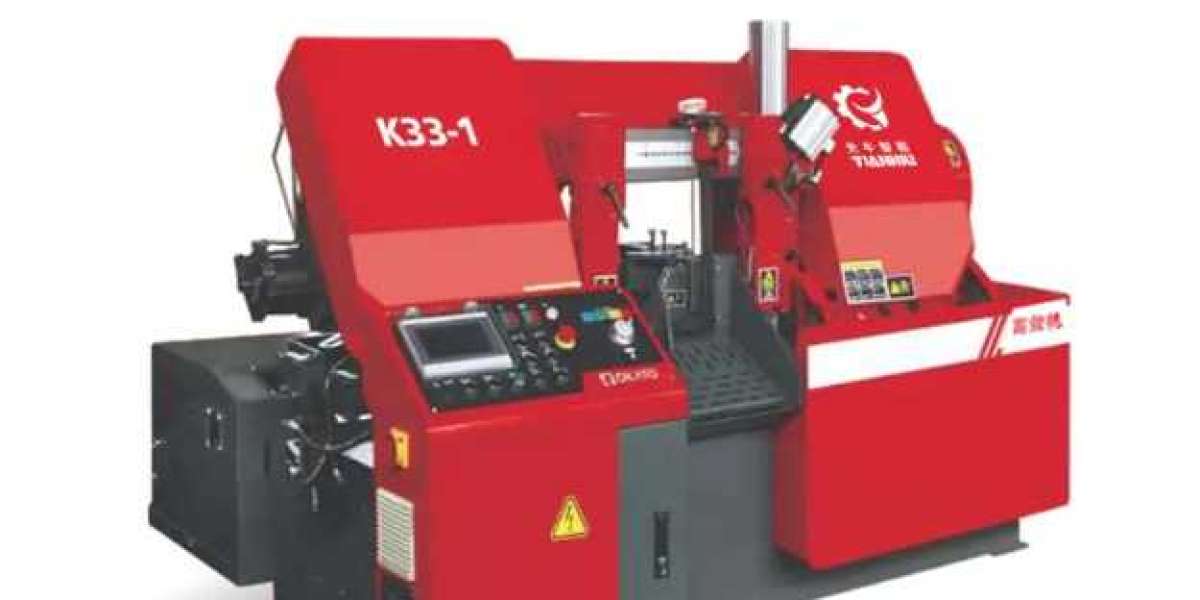
In the bustling environment of a workshop, the small bandsaw machine is a common sight, known for its efficiency and precision in cutting various materials. However, with its operation comes a significant source of noise that can be detrimental to the health and comfort of workers. Noise control technologies for small bandsaw machines have thus become a critical area of focus for manufacturers and users alike. This article delves into the various strategies and technologies employed to minimize the noise generated by these indispensable tools.
The small bandsaw machine, despite its compact size, can produce noise levels that exceed safe exposure limits, particularly in confined spaces. The primary sources of noise in a small bandsaw machine are the motor, the saw blade, and the interaction between the blade and the material being cut. To address these issues, several noise control technologies have been developed.
One of the most straightforward methods to reduce noise is through the use of sound enclosures. These enclosures are designed to surround the small bandsaw machine, effectively dampening the sound waves before they can propagate into the surrounding environment. The enclosures are typically made from materials that have high sound absorption properties, such as dense foam or specialized acoustic panels. While this method can be quite effective, it does add to the overall footprint of the small bandsaw machine and may require additional space in the workshop.
Another approach to noise control involves the use of vibration-dampening technologies. Vibration is a significant contributor to the noise generated by a small bandsaw machine, as the motor and the saw blade vibrate at high frequencies during operation. Dampening these vibrations can be achieved through the use of specialized mounts or feet that are designed to absorb and dissipate the energy from the vibrations. These mounts often incorporate materials like rubber or silicone, which have natural vibration-dampening properties.
The design of the small bandsaw machine itself can also play a role in noise reduction. Modern machines often feature more efficient motors that operate at lower speeds, which can result in less noise. Additionally, the use of high-quality bearings and precision engineering can minimize the friction and noise generated by the moving parts of the machine. Some manufacturers have also incorporated noise reduction features into the saw blade itself, such as the use of special tooth designs that cut more quietly.
Electronic noise control technologies are also being explored. Active noise control systems use microphones to pick up the sound waves produced by the small bandsaw machine and generate opposing sound waves that cancel out the original noise. While this technology is still in its infancy for small bandsaw machines, it holds promise for the future of noise reduction in industrial settings.
Maintenance and proper operation of the small bandsaw machine are also crucial for noise control. Regularly lubricating the machine, ensuring that the saw blade is sharp and properly aligned, and using the correct cutting speed for the material being cut can all contribute to reducing the noise generated by the machine. A well-maintained machine not only operates more quietly but also has a longer lifespan and better cutting performance.
Education and awareness among users are also key components of noise control. Many workshops may not be aware of the potential health risks associated with prolonged exposure to noise from small bandsaw machines. Providing information on the proper use of hearing protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, can help mitigate the risks associated with noise exposure.
In conclusion, the quest for quieter small bandsaw machines is an ongoing process that involves a combination of technological innovation, proper machine design, and user education. As the technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more effective noise control solutions for small bandsaw machines, ensuring a safer and more comfortable working environment for all users. The integration of these noise control technologies will not only improve the working conditions in the workshop but also contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of the small bandsaw machine, making it an even more valuable tool in the world of precision cutting.